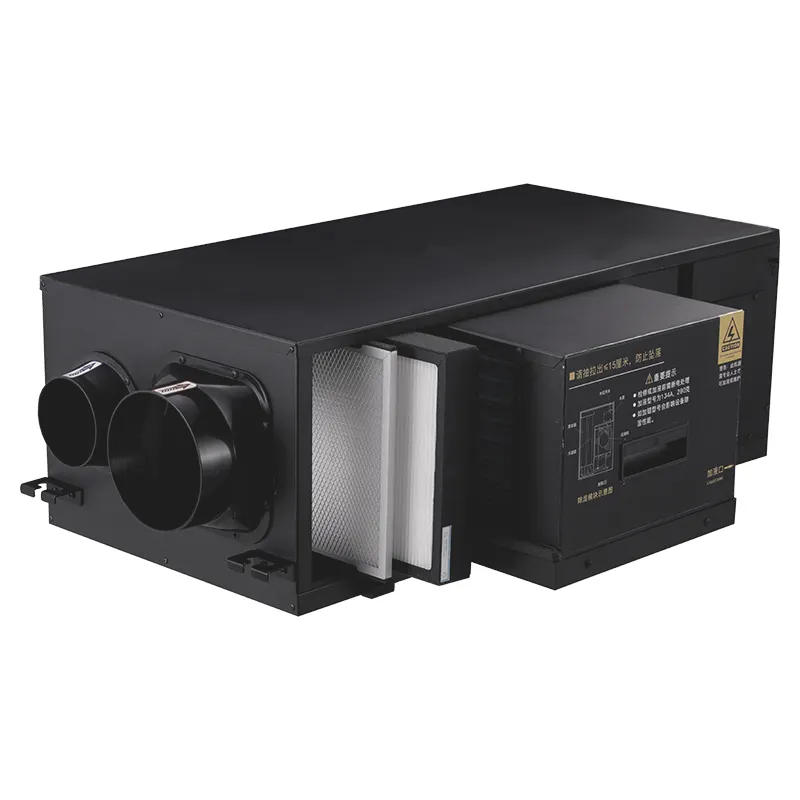
The Hidden Crisis: Indoor Air Quality and the Need for Fresh Air Systems
Understanding indoor air quality (IAQ) management in residential buildings
Managing indoor air quality really starts with understanding how pollutants tend to gather in closed environments. These days most houses are built to save energy, which means they're pretty sealed up tight. Unfortunately, this design traps all sorts of bad stuff inside instead of letting it escape outside. Good ventilation isn't just about opening windows though. It involves controlling where pollution comes from in the first place and making sure fresh air gets circulated regularly throughout the space. When done right, these basic steps stop dangerous particles from building up to levels that can actually make people sick over time. The whole goal is keeping breathing air clean enough so nobody ends up dealing with respiratory issues or other health problems caused by poor indoor conditions.
Pollutant level monitoring (PM2.5, CO2, VOCs) in modern homes
The latest sensor technology makes it possible to detect important pollutants on the spot, including things like fine particles known as PM2.5, carbon dioxide levels (CO2), and those tricky volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that hang around indoors. Research shows something pretty concerning happens when these numbers get too high. For instance, once CO2 climbs above 1,000 parts per million or PM2.5 goes beyond 12 micrograms per cubic meter according to what the Environmental Protection Agency says is safe, people start thinking worse. Some studies point to cognitive abilities dropping by about 15% under these conditions. That's why having continuous monitoring in place matters so much. These systems give warnings ahead of time, which means building managers can take action before poor air quality actually starts affecting how people feel or perform their work.
The health impact of poor ventilation and rising indoor pollutants
Studies show that indoor pollution can reach levels 2-5 times what we find outside according to BMC Public Health research from last year. People spending long hours indoors face about a 40% greater chance of developing breathing problems, especially kids with asthma or elderly folks with weakened immune systems. Climate change is making buildings leakier as extreme weather damages construction materials, so good airflow isn't just nice to have anymore it's practically necessary to cut down on asthma flare ups and stop germs from spreading throughout homes. Whole house ventilation systems tackle this problem by swapping stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while filtering out pollutants along the way. These systems act like invisible bodyguards for everyone living in the space, though they do require regular maintenance to keep working properly over time.
Smart Ventilation: How IoT and Sensors Power Intelligent Fresh Air Systems

Smart Ventilation and IoT-Enabled Controls for Real-Time Response
Today's fresh air systems come equipped with smart controls connected through the internet of things, allowing them to adapt as conditions inside buildings change. These systems have tiny computers built in that check out temperature readings, moisture levels, and how many people are actually in the space, then react almost instantly. Take carbon dioxide for instance. When levels get over 1000 parts per million which we know can start affecting brain function, these smart systems kick into high gear and bring in more fresh air from outside. Research published last year showed that buildings using this kind of intelligent ventilation save about 22 percent on energy costs compared to old fashioned timer based systems. And besides saving money, they also create healthier environments for everyone inside.
Sensor Integration for Air Quality Monitoring and Automation
Modern sensor networks are capable of picking up PM2.5 particles, VOCs, and even tiny amounts of formaldehyde down to just 0.1 micrograms per cubic meter. The data collected gets sent to central monitoring systems which then link sudden pollution increases to common household activities such as cooking meals or doing some spring cleaning around the house. Take for example when particulate matter starts climbing in concentration. The system automatically kicks in HEPA filters long before anyone notices anything wrong with the air quality, keeping PM2.5 levels well under the World Health Organization's safety threshold of 25 micrograms per cubic meter. What we're seeing here is essentially smart ventilation technology that manages itself based on what it detects in the environment.
Demand-Controlled Ventilation and Real-Time Monitoring for Efficiency
Demand controlled ventilation works smarter by directing airflow where people actually are, cutting down energy costs somewhere between 18 and 34 percent based on those latest ASHRAE numbers from 2024. Homeowners can now spot problems easily thanks to real time dashboards showing when filters get dirty or ducts start leaking air. Some top end systems go one step further by checking weather reports ahead of time, warming or cooling outside air before it enters the house during cheaper electricity periods. These smart adjustments mean better indoor air quality while saving money on utility bills too. The whole system adapts to what's happening around it rather than running full blast all day long.
This intelligent layer turns ventilation from a passive utility into an adaptive shield against indoor pollutants—a critical evolution for health-conscious smart homes.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in Fresh Air System Design

Heat Recovery and Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) Explained
Energy Recovery Ventilators, or ERVs for short, work their magic by moving both heat (what we call sensible energy) and moisture (the latent kind) from the air going out to the fresh air coming in. What does this mean? Well, homes actually use 30 to 50 percent less energy on heating and cooling systems when ERVs are installed versus regular ventilation methods. The real kicker though is how much carbon dioxide these systems can save us from emitting into the atmosphere. According to research published by MDPI last year, each home equipped with an ERV avoids around 600 kilograms of CO2 every single year. That's why many green building experts consider ERVs essential components in any serious effort toward creating eco-friendly living spaces.
Energy-Efficient Ventilation Systems Reducing Carbon Footprint
Smart integration drives modern ventilation efficiency. High-efficiency MERV-13 filters, paired with low-power ECM motors, reduce energy consumption by 20–35%. Variable-speed controls adjust airflow based on real-time occupancy, eliminating over-ventilation. Since building ventilation accounts for nearly 30% of commercial energy use, these optimizations play a vital role in achieving global net-zero targets.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Ventilation Solutions for Smart Homes
The latest systems bring together energy recovery techniques with renewable energy sources. We're seeing things like solar powered ERVs (energy recovery ventilators) and geothermal pre conditioning units that work with nature's own temperature differences. Smart systems actually look at what's happening inside buildings, check the weather ahead of time, and even watch electricity prices so they can cut down on how much power comes from the main grid. The savings from these kinds of improvements can reach around 60-65% for operations costs. Plus, manufacturers are starting to use greener stuff in their products too bamboo based filters and old aluminum parts remade into housing components for these systems.
From Detection to Action: AI-Driven Air Quality Response in Smart Homes
Real-time air quality prediction using AI and sensor networks
Smart machine learning tools look at sensor data across different locations to spot when air quality is about to change somewhere between 15 to 30 minutes ahead of time. When these systems see that fine particles called PM2.5 are getting close to going over the World Health Organization's safe limit of 12 micrograms per cubic meter, they kick in the filters early. The latest report on smart indoor air quality systems from 2024 shows something pretty impressive actually - these AI powered setups cut down on bad air spikes by around two thirds. They do this mainly by turning fans on automatically and adjusting how fresh air comes into buildings based on what's happening outside.
Air quality monitors for real-time pollutant detection (PM2.5, VOCs, CO2)
Advanced monitors deliver lab-grade accuracy across multiple pollutants:
| Pollutant | Detection Range | Health Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 0–1,000 μg/m³ | <12 μg/m³ (WHO) |
| CO2 | 400–5,000 ppm | <1,000 ppm |
| VOCs | 0–2,000 ppb | <500 ppb |
This precision enables zoned responses—such as boosting kitchen ventilation during cooking—without affecting other areas, ensuring targeted and efficient air quality management.
Integration of air purification with ventilation systems for comprehensive cleaning
Top-tier systems combine MERV-13 filtration with ERVs, removing 94% of airborne particles while recovering 80% of thermal energy. Smart integration allows:
- Automatic purifier activation when outdoor PM2.5 exceeds indoor levels
- ERV bypass during clean-air periods to enable natural ventilation
- Humidity-linked ventilation to maintain levels below 60% RH and prevent mold growth
Case Study: Smart IAQ solutions in residential applications
A 12-month trial across 85 homes demonstrated:
- 41% reduction in HVAC energy use through demand-controlled ventilation
- 73% fewer PM2.5 exceedance events compared to traditional systems
- 58% faster VOC clearance during pollution incidents
The AI platform adjusted airflow using real-time occupancy and outdoor air quality data, keeping CO  levels below 900 ppm 92% of the time.
Health and Comfort: How Fresh Air Systems Enhance Occupant Wellbeing
Ventilation strategies for improving occupant health and comfort
Good ventilation design keeps the air moving consistently, swapping out old indoor air for fresh stuff from outside that's been properly filtered. What this does is cut down on allergens floating around while keeping temperatures steady and humidity at comfortable levels throughout the space. Some systems now come equipped with smart tech that adjusts airflow based on who's actually present in different areas of a building. These kinds of setups help avoid those awkward situations where parts of an office feel stuffy while others are overly drafty, which can really sap people's energy during work hours. The concept behind demand controlled ventilation makes sense because it creates better living/working environments without guzzling unnecessary amounts of power. Manufacturers these days are increasingly focused on finding solutions that hit all three marks simultaneously health benefits, occupant satisfaction, and operational savings.
Reducing indoor pollutants to improve respiratory health
The bad stuff we breathe indoors, including PM2.5 particles, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and carbon dioxide, really takes a toll on our lungs and breathing ability. Studies indicate that when PM10 levels go up by just 10 micrograms per cubic meter, there's about a 0.8 to 3 percent jump in adult deaths each day according to research published in the Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition back in 2023. Better ventilation systems work hard to suck out all those nasty particles and replace them with fresh, filtered air, which cuts down our contact with harmful substances. Regularly changing the air like this can stop long term breathing problems before they start, especially important for people with asthma or other sensitivities who get triggered easily by poor indoor air quality.
Mould prevention and humidity control through intelligent ventilation
Too much moisture leads to mold problems and dust mites, which are big troublemakers for people with allergies or breathing issues. The newer smart ventilation systems have built-in sensors that check the humidity level all the time. When things get too damp beyond that sweet spot of around 40 to 60 percent, these systems kick in and start exchanging air. This helps stop those wet conditions from forming where mold really loves to grow, especially in places we all know too well like bathrooms after showers or in basement corners that tend to stay dark and damp. Keeping this kind of control actually protects not just our health but also the structure of buildings themselves over time, creating spaces where folks can breathe easier without worrying about musty smells or hidden allergens lurking in walls.
FAQ
What is indoor air quality (IAQ) and why is it important?
Indoor air quality refers to the condition of the air within buildings and structures, especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants. It is important because poor IAQ can lead to health issues such as respiratory problems, headaches, and fatigue.
How do smart ventilation systems improve air quality?
Smart ventilation systems use sensors and IoT technology to monitor and control the air quality in real-time. They adjust ventilation based on pollutants levels and occupancy, ensuring that fresh air is circulated and that indoor air pollutants are minimized.
What are PM2.5, VOCs, and CO2, and why are they important in air quality monitoring?
PM2.5 are fine particulate matters that can penetrate deep into the lungs, VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) are emitted from many indoor chemical products, and CO2 levels can indicate the freshness of air. Monitoring these helps in understanding and improving indoor air quality.
How can ventilation systems be energy efficient?
Ventilation systems can be energy efficient by incorporating technologies like Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs), smart controls for demand-based ventilation, and integration with renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on grid electricity.
What health benefits do fresh air systems offer?
Fresh air systems enhance occupant wellbeing by reducing indoor pollutants, improving respiratory health, preventing mold growth, and maintaining comfortable humidity levels.
Table of Contents
- The Hidden Crisis: Indoor Air Quality and the Need for Fresh Air Systems
- Smart Ventilation: How IoT and Sensors Power Intelligent Fresh Air Systems
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in Fresh Air System Design
- From Detection to Action: AI-Driven Air Quality Response in Smart Homes
- Health and Comfort: How Fresh Air Systems Enhance Occupant Wellbeing
- FAQ
 EN
EN